- Overview of Tableau
- Key Features of Tableau
- Benefits of Using Tableau for Data Visualization and Analytics
- Examples of Industries and Use Cases Where Tableau Excels
- Overview of MicroStrategy
- Key Features of MicroStrategy
- Benefits of Using MicroStrategy for Data Visualization and Analytics
- Examples of Industries and Use Cases where MicroStrategy Excels
- Comparison of Key Features
- Pricing and Licensing Options
- Limitations and Challenges
- Final Thoughts
Overview of Tableau:
Tableau is known to be a leading data visualization and analytics tool. With the help of Tableau, users can easily analyze, visualize, and share data insights in an intuitive and user-friendly manner. Tableau offers a wide range of powerful features and capabilities that have made it a popular choice among businesses and professionals in different industries.
Key Features of Tableau:
Key features include;
1. Interactive Visualization:
By using Tableau, you get access to a wide range of interactive charts, graphs, and visual elements that let users explore and understand data in the most effective possible manner.
2. Drag-and-Drop Interface:
Tableau’s drag-and-drop interface allows users to create visualizations easily. With that, it also enables them to create interactive dashboards without having to do complex coding or scripting.
3. Data Connectivity:
This is another feature offered by Tableau. By supporting connectivity to different data sources, it allows users to access and analyze data from different sources. These data sources include spreadsheets, cloud services, databases, and big data platforms.
4. Advanced Analytics:
Tableau gives users access to advanced analytics capabilities like data blending, forecasting, predictive modeling, and statistical analysis that empower users to get access to deeper insights from the data.
5. Collaboration and Sharing:
With the help of Tableau, users can share dashboards and visualizations with their colleagues and stakeholders. This facilitates collaboration and decision-making processes.
6. Mobile Compatibility:
Tableau offers mobile-friendly versions and apps that allow users to access and interact with their visualizations on their smartphones and tablets.

Benefits of Using Tableau for Data Visualization and Analytics:
Benefits of using Tableau include;
1. Easy-to-Use:
Tableau offers an intuitive interface and drag-and-drop functionality. This makes it easily accessible to users of all skill levels whether you are a beginner or advanced analyst.
2. Rapid Insights:
With the help of Tableau’s powerful data visualization capabilities, users can quickly uncover patterns, trends, and actionable insights.
3. Interactive Dashboards:
Users by using Tableau can create interactive dashboards that easily provide real-time data updates. It also enables dynamic exploration of information.
4. Data-Driven Storytelling:
Tableau allows users to create compelling narratives. This is done by combining data visualizations into a cohesive story that enhances communication and understanding.
5. Scalability:
Tableau is a scalable visualization tool. This means it has the ability to handle large datasets making it a number one choice for organizations of all sizes.
Examples of Industries and Use Cases Where Tableau Excels:
Tableau because of its amazing features excels in many industries including;
1. Retail and E-commerce:
Tableau helps retailers in analyzing sales data. With that, it helps them monitor inventory levels and identify customer trends that can optimize pricing, product assortment, and marketing strategies.
2. Finance and Banking:
Tableau helps financial institutions in analyzing and visualize financial data. It helps them detect fraud patterns and even generate insights for risk management and compliance purposes.
3. Healthcare:
Tableau is widely used in the healthcare sector for different purposes. This includes analyzing data of patients, optimizing resource allocation, tracking disease outbreaks, and improving overall operational efficiency.
4. Marketing and Advertising:
Tableau allows marketers to analyze campaign performance. With that, they can track customer behavior and measure the overall effectiveness of marketing initiatives.
5. Education and Research:
Tableau has proven itself to be valuable in educational institutions and research organizations as well. It helps them visualize data, conduct all kinds of data-driven research, and present findings to the stakeholders.
As you can see tableau’s versatility and the ability to offer a broad range of applications make it a very valuable and preferred tool across different industries. It easily helps professionals in making data-driven decisions and gain valuable insights from the data.
Overview of MicroStrategy:
MicroStrategy as we speak is a comprehensive enterprise analytics and mobility platform. It aims to provide organizations with powerful tools for not only data visualization but analytics and business intelligence purposes. With that, it offers a wide range of engaging features and capabilities that help businesses make informed business decisions.
Key Features of MicroStrategy:
It includes;
1. Business Intelligence and Reporting:
MicroStrategy has the ability to offer robust business intelligence capabilities that allow users to create interactive reports, dashboards, and scorecards. This then helps them monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) and even track business metrics.
Check out our MicroStrategy course options to find the perfect fit for your learning needs and career goals.
2. Data Visualization:
MicroStrategy offers advanced data visualization features to users which then allows them to create visually appealing and interactive charts. They can also make engaging graphs and maps for exploring and communicating data insights effectively.
3. Mobile Analytics:
MicroStrategy by supporting mobile analytics enables users to access and interact with dashboards and reports on their smartphones and tablets. This ensures data accessibility and real-time insights on the go.
4. Advanced Analytics:
By offering advanced analytics functionalities, MicroStrategy empowers its users to uncover patterns, trends, and predictions from their data. These functionalities include predictive analytics, statistical modeling, and data mining.
5. Data Discovery and Exploration:
MicroStrategy allows users to not only explore but discover hidden insights. This is done through self-service analytics that allows them to analyze data from multiple sources and then drill down into details for a more feasible understanding.
6. Data Governance and Security:
MicroStrategy offers robust data governance and security features that ensure data integrity, privacy, and compliance with industry regulations.
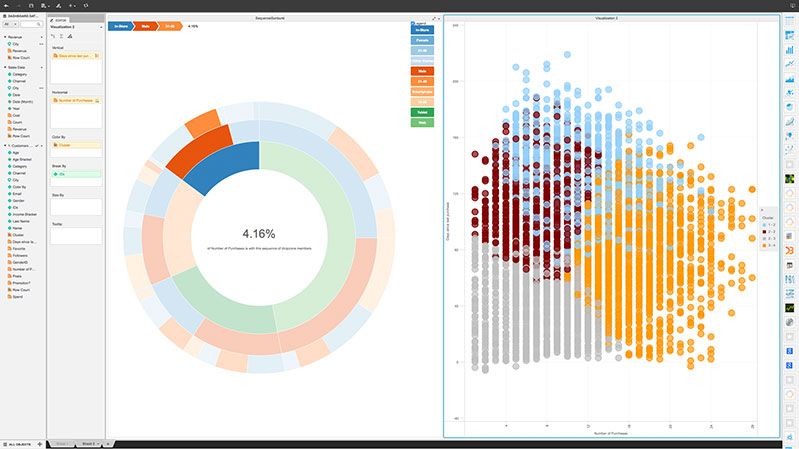
Benefits of Using MicroStrategy for Data Visualization and Analytics:
1. Scalability and Performance:
MicroStrategy has been specially designed to handle large-scale data sets and thus it has the ability to support thousands of users concurrently. This makes it suitable for all such organizations that have complex data.
2. Centralized Data Management:
Organizations can centralize their data sources through MicroStrategy and then create a single version of truth ensuring data consistency.
3. Real-Time Insights:
With MicroStrategy, you can do real-time data analysis and reporting.
4. Collaboration and Sharing:
The collaboration feature allows users to share reports, dashboards, and insights with colleagues and stakeholders. This fosters a collaborative data-driven culture.
5. Embedded Analytics:
MicroStrategy offers the flexibility to embed analytics into other applications and systems. This allows businesses to integrate data insights directly into the existing workflows and applications.
Examples of Industries and Use Cases where MicroStrategy Excels:
1. Financial Services:
MicroStrategy is used in the financial services industry for different purposes including fraud detection, risk management, portfolio analysis, and regulatory compliance reporting.
2. Retail and Consumer Goods:
Based on customer behavior and preferences, MicroStrategy helps retailers analyze their sales data and personalize marketing campaigns.
3. Healthcare and Life Sciences:
In healthcare organizations, MicroStrategy is implemented for data analysis and operational efficiency improvement.
4. Manufacturing and Supply Chain:
Manufacturers using MicroStrategy can monitor production metrics and perform predictive maintenance analysis.
5. Government and Public Sector:
Government agencies use MicroStrategy for data-driven policy-making and performance management.
The amazing features offered by MicroStrategy make it a very powerful tool for organizations to use across various industries for making informed business decisions.
 Fundamentals of Visualization with Tableau
Fundamentals of Visualization with Tableau
- University of California via Coursera
- 11 hours of effort required
- 111,158+ already enrolled!
- ★★★★★ (4,671 Ratings)
 Data Visualization and Communication with Tableau
Data Visualization and Communication with Tableau
- Duke University via Coursera
- 25 hours of effort required
- 175,244+ already enrolled!
- ★★★★★ (2,852 Ratings)
 Tableau A-Z: Hands on Tableau Training for Data Science
Tableau A-Z: Hands on Tableau Training for Data Science
- Kirill Eremenko via Udemy
- 9 hours on demand videos
- 230,147+ already enrolled!
- ★★★★★ (60,907 ratings)
Comparison of Key Features:
1. User Interface and Ease of Use:
Tableau:
With Tableau, you get access to a user-friendly and intuitive interface that allows users to create visually appealing and interactive visualizations easily. It has drag-and-drop functionality that allows users to build charts, graphs, and dashboards.
MicroStrategy:
It also provides a user-friendly interface along with a wide range of pre-built templates and visualizations.
2. Data Connectivity and Integration Capabilities:
Tableau:
Tableau offers strong data connectivity capabilities that allow users to connect to a wide range of data sources.
MicroStrategy:
With MicroStrategy, you get extensive data connectivity options that allow users to connect to different data sources.
3. Data Visualization and Dashboard Creation:
Tableau:
Tableau is quite popular for its powerful data visualization capabilities offering a wide range of visualizations. You can create dynamic visualizations by dragging and dropping data elements onto the canvas.
MicroStrategy:
MicroStrategy gives you access to robust data visualization features allowing users to create visually appealing scorecards, reports, and dashboards.
4. Advanced Analytics and Business Intelligence Capabilities:
Tableau:
Tableau offers advanced analytics capabilities that include data blending, statistical modeling, and forecasting allowing users to perform complex calculations and do so much more.
MicroStrategy:
Offering advanced analytics functionalities and providing users with the ability to perform advanced calculations.
5. Collaboration and Sharing Features:
Tableau:
Tableau gives users access to collaboration features for sharing dashboards, reports, and visualizations with others. It also allows collaboration in real-time.
MicroStrategy:
MicroStrategy provides robust collaboration features that allow users to collaborate on reports and dashboards. Other features like annotations and discussions make it easier for teams to collaborate.
6. Mobile and Cloud Capabilities:
Tableau:
Tableau offers efficient mobile capabilities that allow users to access and interact with dashboards on their mobile phones.
MicroStrategy:
MicroStrategy on the other hand also offers comprehensive mobile support that gives users the option to access and interact with dashboards and reports on mobiles.
From the above-given information, we can say both tools offer powerful data visualization, analytics, and business intelligence features. So the decision is entirely up to the user based on specific requirements like data connectivity needs, user interface preference, and more. So you can evaluate these features and then make an informed decision.
Pricing and Licensing Options:
Comparison of pricing models for Tableau and MicroStrategy:
Tableau:
Tableau offers multiple pricing options. It includes both perpetual and subscription licenses. The pricing is entirely based on the edition and the number of users and the cost varies depending on factors like feature requirement, deployment type, and additional add-ons.
MicroStrategy:
MicroStrategy on the other hand also offers flexible pricing options including perpetual and subscription licenses. It offers different pricing editions with varying features and specific modules or functionalities that allow organizations to choose the most suitable option.
Different Licensing Options for Each Platform:
Tableau:
Tableau offers two licensing options;
a. Creator License:
It is designed for all those users who wish to create and publish content. It allows users to develop dashboards and reports by giving full authoring capabilities.
b. Explorer License:
With this license, users can explore and interact with visualizations and reports created by Creator license users.
With that, tableau also offers viewer licenses that are suitable for users who need to view and consume published content without having to create or modify it.
MicroStrategy:
MicroStrategy offers different licensing options that meet different requirements of users.
a. Desktop License:
With this license, users can develop and design visualizations and reports on their desktop machines. It gives individual users full authoring capabilities.
b. Web License:
Taking this license will give users access and the ability to interact with reports and dashboards through web browsers. This type of license is suitable for users who consume and analyze data through the web interface.
c. Mobile License:
This license lets users access and interact with reports and dashboards on their mobile devices.
d. Server License:
Server license allows users to deploy and manage the MicroStrategy platform on-premises or in the cloud. It offers features for scalability, administration, and security purposes.
Please note that specific pricing and licensing options might vary based on the vendor’s offerings, edition, region, and any promotional discounts or packages available.
Whenever considering the pricing and licensing options of Tableau and MicroStrategy, it is best for organizations to carefully evaluate their budget, long-term scalability, and user requirements.
Limitations and Challenges:
Limitations and Challenges of Using Tableau:
1. Data Size and Performance:
When handling extremely large datasets or doing complex calculations, tableau may face some challenges and this can impact the overall performance and responsiveness.
2. Steep Learning Curve:
Yes, tableau does offer a user-friendly interface but mastering its advanced features and functionalities requires a significant learning curve for new users.
3. Cost:
Since the cost of Tableau is a little high, it can be a limitation for small or budget-constrained organizations.
4. Data Preparation:
Tableau’s data preparation capabilities are not as robust as compared to dedicated data preparation tools. And this may require data transformations and clean outside of Tableau.
Limitations and Challenges of Using MicroStrategy:
1. Complexity:
MicroStrategy’s extensive features can sometimes lead to a steep learning curve for users and especially for those who are new to business intelligence tools.
2. Initial Setup and Configuration:
Setting and configuration are quite complex and thus required proper planning and IT resources.
3. Limited Visualization and Customization:
MicroStrategy does offer a variety of visualization options but the level of customization may be limited as compared to other tools.
4. Upgrading and Migration:
Upgrading to newer versions or migrating from older ones can be complex and time-consuming and requires careful planning and testing.
5. Cost:
The cost of licensing and overall maintenance of MicroStrategy is higher as compared to other business intelligence tools.
Organizations before deciding which one to choose should consider the limitations of both Tableau and MicroStrategy. That is why it is suggested to conduct a thorough analysis of specific requirements, resources, and long-term goals as it can help in making informed decisions.
Final Thoughts
Even after reading this entire article, the choice between Tableau and MicroStrategy entirely depends on the organization’s specific requirements. What we have done here is give our readers a thorough overview of both tools and what they offer. Now it is recommended to conduct a thorough evaluation that includes pilot testing and gathering feedback from key stakeholders. This will ensure that the selected platform aligns with the objectives of the organization.
Important note: Readers should know that this entire comparison is based on the features and information available at the time of writing. So it is recommended to review the latest updates, new releases, and customer reviews of Tableau and MicroStrategy at the time of making a decision. This would be better for the organization’s well-being.






